(Click the poster above to download it in Arabic)
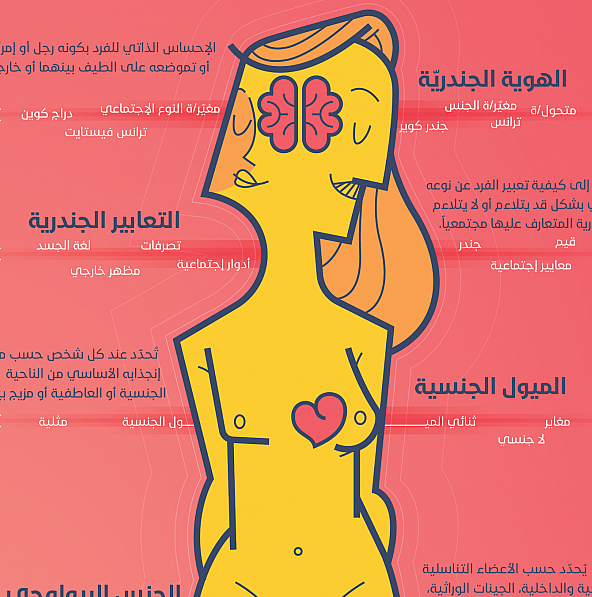
Sexual Identity:
A term that describes a person’s perception of the many different aspects of their sexuality. There are many components to sexual identity, each carrying its own meaning that evolves and develops throughout a person’s life.
Biological Sex:
A social construct that categorizes people based on their internal and external sex organs, genes, and sex chromosomes, as well as sex hormones. Most people are born with a relative “congruence” between their genetic/biological and hormonal makeup, and are therefore classified as “male” or “female.” The medical system and society at large usually choose to determine a person’s biological sex as “male” or “female” according to their external sex organs. In reality, people are born with diverse biological, chromosomal, and/or hormonal differences, or variances in their secondary sex characteristics. Many of these people cannot be conclusively assigned “male” or “female” at birth according to medical, legal, and/or social standards. The medical term intersex is often used to describe them.
Gender / Gender Expression:
Gender is a social construct that translates the “biological sex” assigned to a person into a sort of “social sex.” The process is determined by a number of norms, values, symbols, and roles that determine who is a “man” or a “woman” in a society. Gender also determines how “masculinity” and “femininity” are expressed, and the hierarchical relationship between those two concepts. Through socialization, we all learn how to act and appear according to the gender assigned to us based on our assigned biological sex.
Gender Expression describes how a person expresses themselves in a way that may or may not fit with their assigned gender, based on the gender norms in their society. These norms may evolve and change, but they remain mostly binary. People whose gender expression challenges these social norms are often punished and chastised.
Sexual Orientation:
Sexual Orientation is determined based on the central sexual and/or romantic attraction that a person experiences. In general, a person can experience attraction: to the same sex and describe themself as homosexual; to a different sex and describe themself as heterosexual; to more than one sex (in various degrees) and describe themself as bisexual; or to no sex and describe themself as asexual. These labels generally describe how a person perceives their center of attraction and many people can find themself at different points in this spectrum. However, sexual orientation doesn’t describe sexual behavior, and may not correlate to any specific set of sexual practices. The preferences one may have in sexual relations vary from one person to another.
Gender Identity:
A term that describes the internal feeling of being a “man,” being a “woman,” being somewhere in between those two social constructs, or being somewhere outside of them. Most people usually feel comfortable with their assigned biological sex and/or assigned gender (referred to as cisgender). Although this congruence has varying degrees, it usually remains within the binary of man-woman, masculine-feminine. However, some people don’t feel that they fit in their assigned biological sex and/or assigned gender and may describe themself as transgender. In order to reconcile their bodies and their gender identity and/or to feel more at peace with social expectations, many transgender (or trans) people begin a transition process. This process may involve changing appearance, changing gender expression, hormonal and/or surgical procedures, or other steps a trans person might need to feel more comfortable with their gender identity.
.png)